Artificial Intelligence in Human Experience Management (HXM)
When I ask people if they are familiar with Artificial Intelligence (AI), I often get a positive response but the answer is usually in the context of movies and entertainment. Some great examples exist, Ex machina and WestWorld to name a few but for the normal masses the common understanding of the use of artificial intelligence usually involves a robot or an army of robots trying to take over the world.
When I tell people that I am researching Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning in the context of Human Capital Management (HCM) they often give me a strange look followed by a question if I am building robots to replace Human Resources professionals. That’s an easy no, although there are some functions that HCM professionals can leverage to better do their job and be more efficient with their time leveraging technology including AI. Let’s start there with a basic definition of Artificial Intelligence.
Artificial intelligence is a technology that enables a machine to simulate human behavior. The simplest example of this is a chatbot. You have seen these pop up on on screens from all types of websites offering to help you, including SAP, see sample below.
© Graphic Source SAP

© Graphic Source SAP
Chatbots were originally limited to text-based communication, as the name implies; but, as technology has progressed, this interaction paradigm has expanded to include various input methods such as touch and voice. Chatbots are frequently utilized as a key channel for customer service because they provide consumers with quick, familiar, and conversational access to the businesses they care about 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Anyone who has ever dialed a customer service number and yelled “REPRESENTATIVE!” into the phone, knows that they are in an automated system and often the only way to speak to a human is to ask for a representative.
For starters, building and deploying chatbots are quite commonplace and they leverage Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to follow a simple set of rules (i.e. “if x, then y”) without the need for human intervention. There are many use cases for this type of automation, including for Human Capital Management, some of which I detailed in an earlier blog titled What does RPA have to do with HCM and Payroll?
Learning from the data
A more mature example of Artificial Intelligence leverages Machine Learning. Whilst a chatbot is following a direct path or decision tree based on responses input by the human, Machine learning takes it a step further by allowing the machine to automatically learn from past data without programming explicitly, allowing it to solve more complex problems.
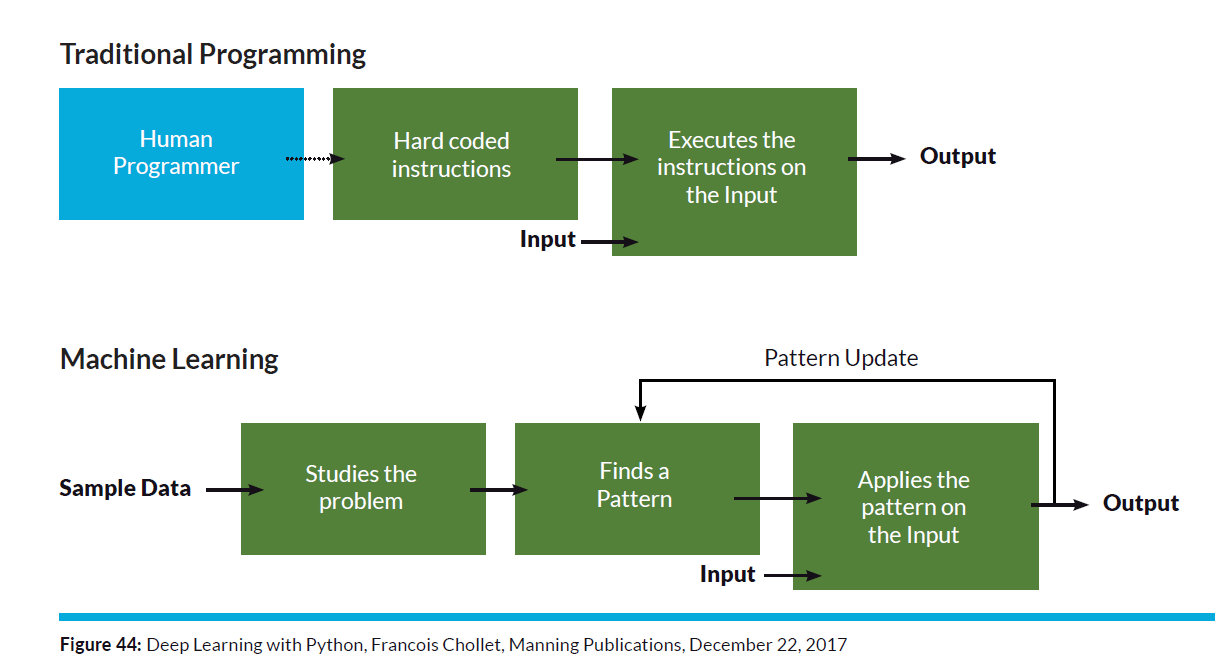
The difference lies in the method as shown in the diagram below. This effectively demonstrates that, for the past 80 years or so, we’ve constructed software systems that begin with the human coder. To automate this labor, people research problems or processes, develop workflows, and code user interfaces, logic, and data-driven algorithms.
© Graphic Source HR Technology 2021: The Definitive Guide Josh Bersin
The opposite occurs with AI and machine learning. The system begins with a piece of data, analyzes it for patterns, and then uses a variety of artificial intelligence to recognize patterns, refine assumptions, and make recommendations. Unlike the algorithmic-centric software we’ve produced in the past, it’s really a data-centric solution.
In the case of HR, this provides us with a wealth of new information regarding all of the personnel decisions we make, such as who to hire, how much to pay people, what job to pursue, what courses to pursue, who to promote, and so on. These kinds of algorithms are now being incorporated into HR platforms, so the tools you buy are becoming smarter. Because they rely on data, as this graphic indicates, if your systems architecture is fractured, you’ll have a slew of prediction and recommendation machines scattered throughout your organization.
As the technology develops, employers are doing a better job of taking data from various areas to make better decisions. I had the opportunity to showcase a great example of this is in the session I gave at SAP TechEd in 2021, where I explained how SAP SuccessFactors customers utilized COVID data from the World Health Organization in tandem with their critical employee HR & Payroll data via SAP analytics Cloud to predict which employees and locations were potentially at risk and even used that data to perform predictions including Leave liability analyses as detailed in this blog: The COVID-19 Impact: Identify Leave Liability Costs.
How can we use machine learning in Human Experience Management HXM?
First you need to focus your mindset on the difference between backward looking business intelligence and forward looking machine learning. Traditional analytics might provide you with a turnover rate whilst a machine learning output would help you identify which specific employees are most likely to leave giving you an opportunity to be proactive to engage them.
Human Experience Management
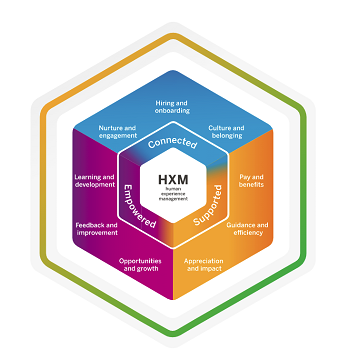
Previously, HR software was created for HR managers; now, it is designed for employees and more specifically for the experience of those employees. SAP SuccessFactors model for Human Experience Management, shown below, is designed to ensure that employees feel connected, supported and empowered through the various stages of their employment lifecycle.
© Graphic Source SAP
Below I have created a quick reference sample of use cases for those employee stages leveraging Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
Sample Machine Learning Use Cases for Human Experience Management (HXM)
| Process | Description | Example AI use case |
| Hiring & Onboarding | Nurture candidates to secure the best talent and drive productivity from the start with personalized onboarding. | Time to fill estimations
AI can be used to anticipate how long it may take to fill a job demand based on historical data for the type of role, its requirements, geography etc. Recruiters will be able to reprioritize as needed. |
| Culture and belonging | Help people align with company goals, collaborate more easily, and feel a sense of belonging | Employee Productivity Spurts
Different groups of employees are more productive at different times throughout the day. This can vary based on geography, age demographics, departments etc. Leverage machine learning and employee system engagement (click vs idle tracking) to determine these algorithms and schedule employee activities, engagements and work schedules accordingly. |
| Pay and Benefits | People pay accurately on-time, and optimize benefits according to people’s unique needs | Compensation Planning
A wide range of issues must be carefully considered when making effective compensation judgments. These criteria include the market pricing for the skills, how in demand the skills are, and the model of compensation that is applied. AI can be used to evaluate employee skills, the market rate for those skills, and whether those skills are in increasing or decreasing demand and financial factors like the cost to replace to make optimal overall compensation selections that reflect this line of thinking. |
| Guidance and efficiency | Value people’s time by providing recommendations that prompt employees and managers to take the right actions. | Employee Flight Risk Identification
Leveraging company historical data as well as industry statistics and gender age and geographical considerations regarding turnover can be used to determine which active employees may be at the most risk for leaving the organization. |
| Appreciation and impact | Connect people to others, help them get assistance or find answers, and reward them, when, where and how they want. | Assign Mentors with similar History
Statistics say that employees are more engaged in their job, career and to their employer when they have a mentor. Machine learning can be used to identify other employees in the organization that have had similar backgrounds, geography, career progression, previous employers etc. and connect them for mentorship opportunities. |
| Opportunities and growth | Arm managers and HR leaders with insights on how people’s skills can be leveraged and help employees develop and grow. | Positive Chatter Analysis
Chatter analysis can be performed to reveal the top three issues from social media sources (from within a company’s firewall). This provides customized and actionable advice for a specific leader to enhance team engagement. If an employee is recognized for exceptional performance, this too can be detected and amplified including more public praise and acknowledgement for the employer on a larger scale. |
| Feedback and improvement | Make it easy for people to receive and provide continuous feedback and coaching | Negative Chatter Analysis
As opposed to Positive Chatter Analysis, Negative Chatter Analysis can be performed to reveal employees who are consistently mentioned in a negative fashion via company communication channels (Email, slack etc.) Identifying these employees and the performance related concerns can provide the organization an early opportunity to ensure the employees is in the right role and that the employee has what they need to be successful and fill gaps by recommending training and mentoring programs accordingly. |
| Learning and Development | Create a culture of continuous learning by providing everyone access to relevant learning experiences | Skill Identification Data Scraping
Having employees regularly update their internal profiles with their latest skills, certifications etc. is often a manual exercise. Data scraping technology can be used to search internal sources, resumes, sales performance, certifications, badges, likes to easily propose updates to their profiles regularly. Having the latest employee skills available makes it easier for an organization to plan to fill future positions and create career paths. It is feasible to create a heatmap of a company’s skills on a broad scale versus necessary capabilities, and intervention programs can be put in place to allow enterprises to strategize around filling any skill gaps. |
| Nurture and engagement | Use data analytics to understand what people need and take the right actions to drive engagement | Employee Experience Improvements
Analysis of tickets logged and ticket deflection and automated resolutions through intelligent services tracking |
You want to Predict the Future
While coming up with examples like the ones included above, it’s easy to find yourself thinking of both a company’s and an employee’s KPI’s, which is an easy mistake to make. AI and Machine learning are most effectively used to predict the future. When evaluating what use cases are the most beneficial to use for AI, always start with the problem and not the solution.
As a true believer in Data Science and Descriptive, Predictive and Prescriptive analytics, or in other words, as a geek who writes books about the difference between reporting and analytics, I caution the reader to not make the easy mistake of confusing KPIs with prediction targets.

To get started with a great blog that explains the different types of AI, check out Meet SAP’s AI Portfolio and What It Can Do For You. To stay in the know on SAP SuccessFactors latest advancements in the area of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in HR visit http://community.sap.com/topics/artificial-intelligence.

Leave A Comment?
You must be logged in to post a comment.