An employee works each day for an hour longer than is stipulated in his or her collective agreement. The employee is assigned one hour’s time credit for each paid workday. The time credit determined is posted to the time type Compensation Time .
Explanation
|
1 |
D |
VARSTFREE |
|
2 |
N |
D |
VARSTPRSNT |
|
3 |
N N |
|
4 |
N Y |
D |
VARSTDAYTY |
|
5 |
N Y |
HRS=1.00 |
ADDDB2000 |
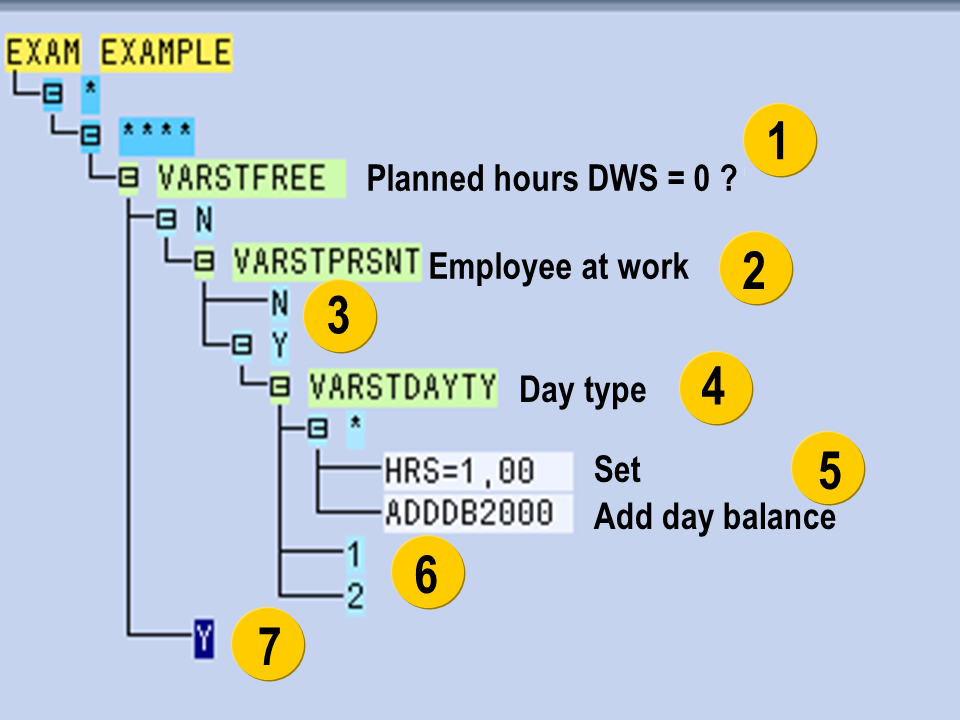
The daily work schedule has more than zero planned working hours. The employee is at work. The day type is either 0, BLANK, (work/paid) or 3 (off/special day).
Operation HRS retrieves an hour. The hour is added to time type 2000 using operation ADDDB.
|
6 |
N Y 1 |
|||||
|
N Y 2 |
|
7 |
Y |
All queried answers must be listed for an operation. Errors can occur if the decision tree is not complete.
You can also give generic answers to a decision tree using an asterisk (*). Please note that the number of asterisks must correspond to the anticipated length of the variable key.

Leave A Comment?
You must be logged in to post a comment.