Welcome to the SAP cost allocation tutorial. In every organization, there are costs involved in various departments. In this tutorial, we will discuss how these costs can be allocated across different SAP cost objects like cost center or internal order and help to create a cost analysis report.
Let us look at a simple example on how cost allocation comes into effect and why it becomes the most integral part of controlling.
CSN Ltd operates as an IT equipment service center for reputed brands across the UK. This company deals with after-sales services including repair and refurbishment services for products like laptops, PC, LCD monitors, etc. CSN Ltd has a division in the UK comprising of departments like Management, Logistics, Warehouse, Service and Quality Control.
Each of the departments has its own mode of operation running daily which incurs significant amount of cost which can be attributed as Direct and also Indirect. CSN management has come out with a strategy on how these costs can be charged to each impacted cost center to come out with the most efficient costing report. This is where cost allocation planning comes to the picture where the company will consider impacted cost centers where costs will be allocated in related proportion. In the allocation planning, amount and quantities will be periodically determined and allocated from sender cost objects (like cost center) to receiver cost objects. In this case, we will be using CSN departments as primary cost centers which will act as both sender and receiver cost objects.
In this tutorial, we will try to understand different cost allocation methods in SAP which a successful organization can adapt in order to get clear insight about its cost accounting report.
- Cost Allocation Cycle
- Cost Allocation – Distribution
- Cost Allocation – Assessment
Basics of SAP Cost Allocation
For a dynamic organization with complex operations where multiple projects / activities are running on daily basis adding up to the company’s profitability, accurate costing flow between related cost objects becomes one of the vital factor to look at when it comes to project based costing. SAP provides the most systematic foundation on how cost allocation process can contribute to the effecting reporting related to cost management.
Let’s take the scenario of CSN Ltd. The following image will give us a good idea on organizational structure of CSN.
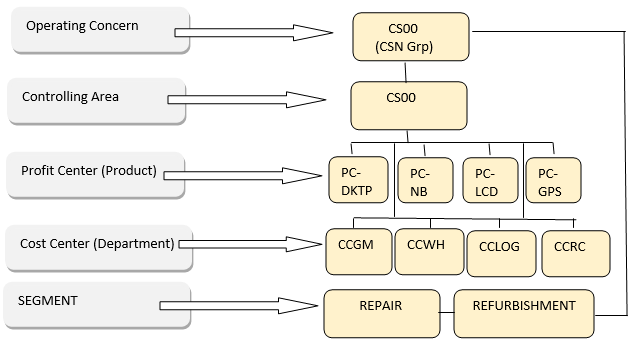
In course of daily operation, various department as given above incur costs which are captured under related cost centers: CCGAM, CCWH, CCLOG, CCRC , CCSERV.
Cost Element Structure
In SAP Cost Allocation process, cost element plays the key role since costs flow from FI direct postings to related cost objects in Controlling. As we know, in Controlling there are two kinds of cost elements.
PRIMARY COST ELEMENT
Being directly associated with G/L, it is linking FI and CO via FI direct posting to related cost objects (cost center, internal order, CO-PA object). In SAP, all primary cost elements are categorized as ‘1’ under CS00 controlling area.
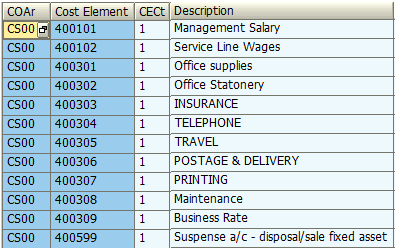
SECONDARY COST ELEMENTS
These cost elements are maintained based on specific category, so that they can be used for reposting, cost assessment and revenues inside the CO.
CSN has also listed specific cost elements in a form of overheads which need to be used and allocated only within controlling area ‘CS00’ to related cost objects.
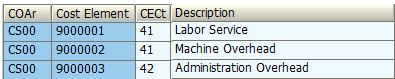
In order to cater to the requirement of cost flow across the related cost objects (FI to CO or within CO), SAP has come out with unique methods of SAP cost allocation.
What is Cost Allocation in SAP?
Within cost center accounting and overhead cost controlling, allocations plays a vital role enabling the business users to periodically allocate amounts and quantities from sender cost objects to receiver cost objects based on cost center allocation planning and structure. Both actual and planning data can be allocated from sender cost object to receiver cost object in SAP cost allocation process using allocation cycle.
SAP Cost Allocation Methods
Taking the above scenario where primary cost elements and secondary cost elements are listed within a company and there is a requirement of correct cost evaluation from operation perspective, SAP recommends the following two types of Cost Allocation process:
- Distribution – for Primary Cost Element
- Assessment – for Secondary Cost Element
SAP Cost Allocation Method – Distribution
Distribution process is mainly used for allocating the amount and quantities (both plan and actual) of one or more sender cost objects to multiple receiver cost objects. Generally, in this type of SAP cost allocation, debit and credit of amount and quantities between sender cost objects (e.g., cost center) and receiver cost objects takes place under the original primary cost element, which means amount in the primary (original) cost element remains the same as before. Let’s consider the following scenario.
CSN has occupied building which is shared by its department as listed above in the structure. Monthly CSN’s building management incurs rental charges for the building which is stated as primary cost element and it needs to be allocated to various department (maintained as cost centers).
To address this requirement, SAP propose to define distribution process within the system since it is related to allocation of costs incurred within primary cost elements.
In SAP, there is customizing related to calculation of both actual and planning overhead rates. On the following screenshot, rates of overhead are related to planning. On the basis of these rates, overhead is allocated.
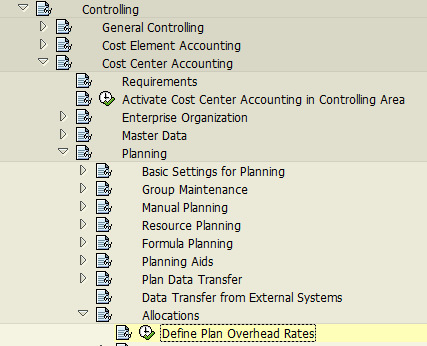
In the following windows, there are multiple options to plan overhead rate.
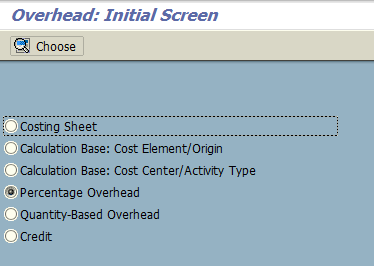
For overhead cost allocation, there are three things we need to maintain as we are in the phase of planning:
- Calculation Base: Cost Elements / Origin
- Calculation Base: Cost Center / Activity Type
- Percentage Overhead
The reason we choose the above options is because for all sorts of allocations methods, a calculation base is required both for cost elements and cost centers. We need percentage rate to be planned for related overheads on the basis of which cost allocation will be carried on.
Now, let’s go back to the scenario where we have to allocate building rental costs of CSN group. We need to first put the related cost element / cost center as the calculation base for CSN rental cost.
Choose the option “Calculation Base: Cost Elements / Origin” and click “New Entries” button. Then, create a new calculation base for CSAD: CS Admin Overhead.
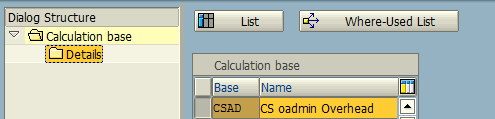
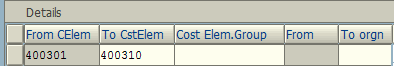
Under the CSN’s controlling area CS00, update the following cost element (Admin O/H) rate as calculation base.
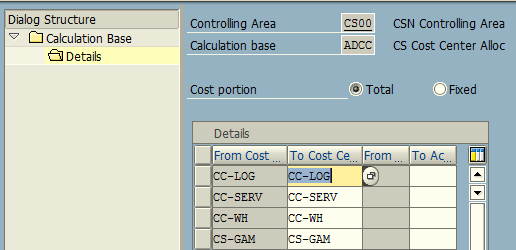
Now, go back to the initial screen and choose the option “Calculation Base: Cost Center / Activity Type”. Create new entries and update the related cost center in this allocation planning.
Finally, choose the option “Percentage Overhead”. In this option, we need to plan the percentage rate at which the CSN Admin Overhead will be allocated.
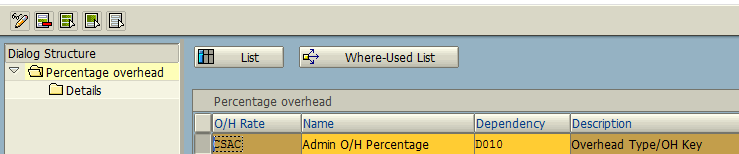
Click Details tab and update Validity Period, Rate of Percentage, Controlling Area, etc.
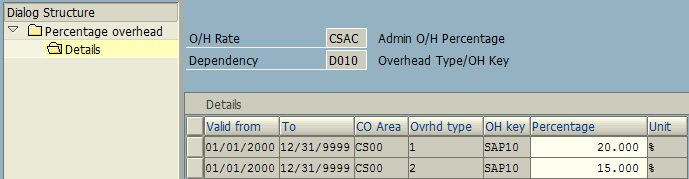
DEFINE DISTRIBUTION CYCLE
We need to define a Distribution Cycle (with a specific naming convention containing up to 6 digits), e.g. CSNRP1.
IMG -> Controlling -> Cost Center Accounting -> Planning -> Allocations -> Distribution -> Define Distribution
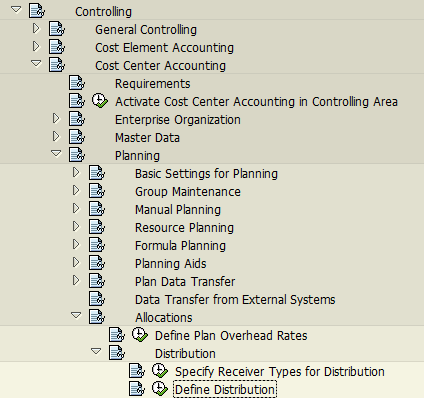
In the next screen, we will choose the option “Create Plan Distribution”.
Choose controlling area CS00.
Next, create a Distribution Cycle (transaction KSV1).
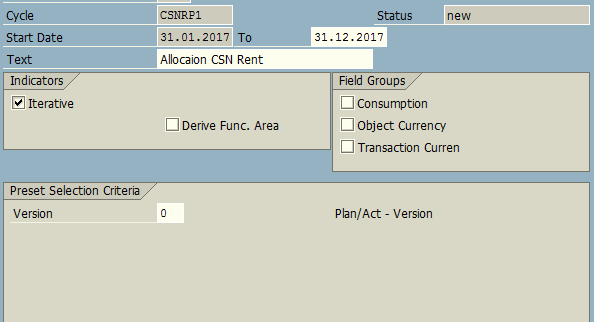
Within the distribution cycle we need to attach a segment consisting of the details of sender and receiver cost centers and cost allocation percentage.
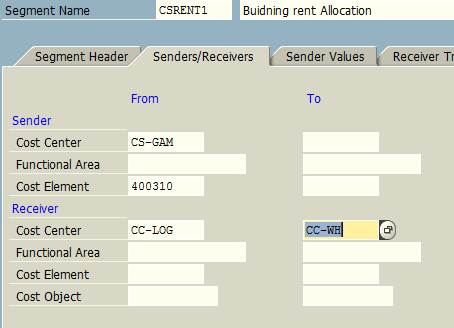
We maintain the following under Senders/Receivers tab:
- Sender cost center: CS-GAM
- Receiver cost centers: CC-LOG (Logistics), CC-WH (Warehouse), CC-SERV (Service Center)
Under Receiver Tracing Factor tab, we specify cost element 400310 – Building Rent which needs to be allocated to the receiving cost centers. Finally, under Receiver Weighing Factor tab, we maintain the receiver cost center and the allotted percentage at which rent cost will be allocated as primary cost element.
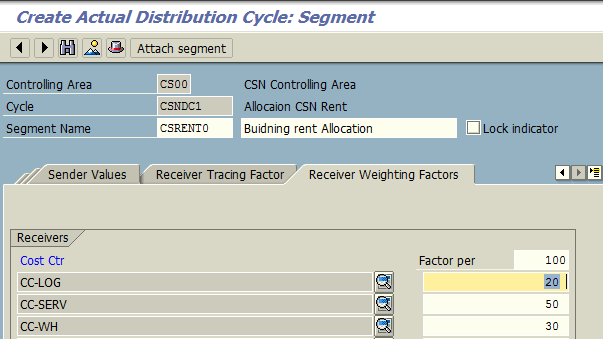
After saving the segment, we can save the distribution cycle.
EXECUTE DISTRIBUTION CYCLE (TRANSACTION KSV5)
This activity is carried out during the period end closing. All distribution cycles are generally executed in order to fulfill the accomplishment of primary cost allocations like the above scenario where CSN rent cost is allocated to receiver cost centers CC-LOG, CC-WH, and CC-SERV based on the percentage allotted in the distribution cycle.
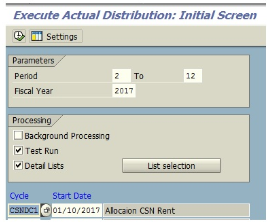
Enter the following data in KSV5 transaction:
- Period: 02 to 12 (Cost allocation will be performed according to the period stated in the distribution cycle)
- Select distribution cycle within the validitiy period
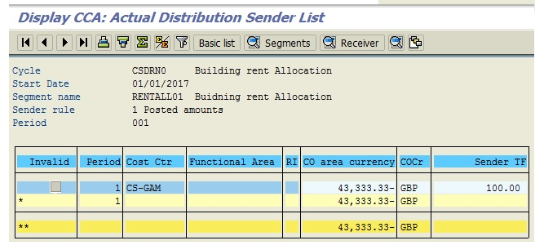
Once executed the system will display the following screen (see below). The screen displays the cycle structure: sender cost center of CSN building rental.
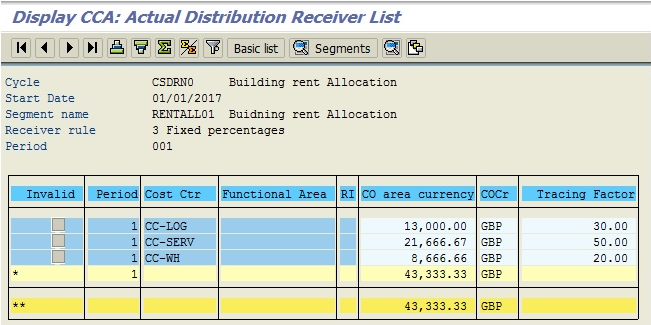
The following screenshot tells how CSN building rental cost is allocated to receiver cost centers CC-LOG, CC-SERV, and CC-WH.
SAP Cost Allocation Method – Assessment
In this method, internal SAP cost allocation is performed based on both primary and secondary cost elements. For example, during product costing we use assessment method to allocate the internal cost from a production cost center to a related production order.
This method is about grouping multiple cost elements and reclassifying them under a secondary cost element.
Process Prerequisites
Create assessment cost element (secondary) and specify receiver types for assessment where we can specify which table fields are active and whether a single value, an interval, or a group can be entered for these fields. You make these settings per controlling area and separately for plan and actual data respectively.
Allocation Structure
Process related to cost allocation via assessment usually requires predefined settings comprising of segment containing a source cost element being assigned to desired assessment cost elements. The whole setup gives the formation of the allocation structure which can be used during assessment cycle definition instead of an assessment cost element in the segment. Usage of allocation structure during assessment cycle setup is always optional and depends on the business scenario.
In SAP system, allocation structure is defined under the following path:
New allocation structures can be created as demonstrated below where we will assign a source cost element and assessment cost element and save the settings.
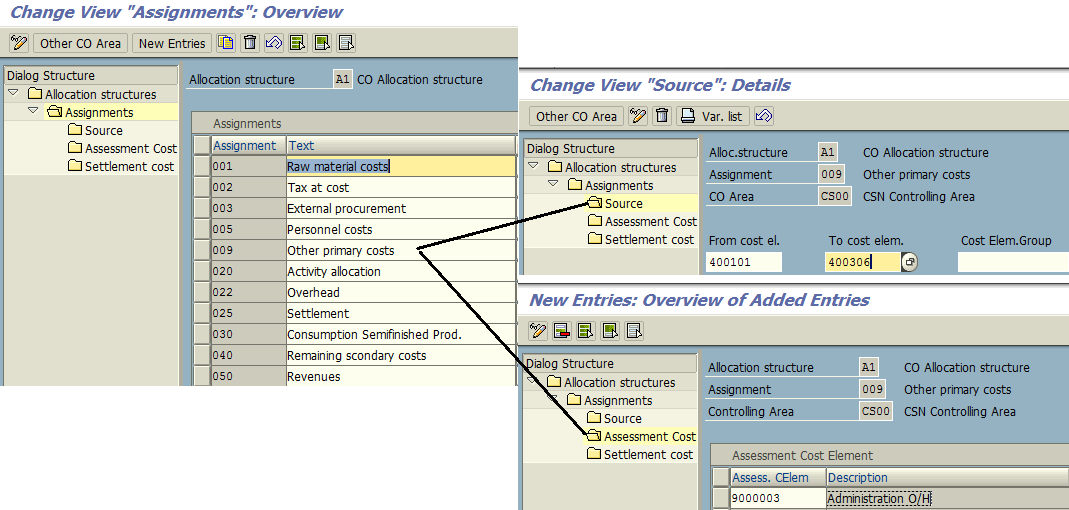
Now, coming back to SAP cost allocation process with assessment method, where cost is allocated using the assessment cost element which generally wipes out the traceability of original cost element at the time when cost is getting allocated from a sender cost center to a receiver cost center. Finally, when the process completes, assessment of cost elements gets updated in both sender and receiver cost centers.
Allocation process continues with creation of plan assessment (transaction KSU7) under controlling area CS00.
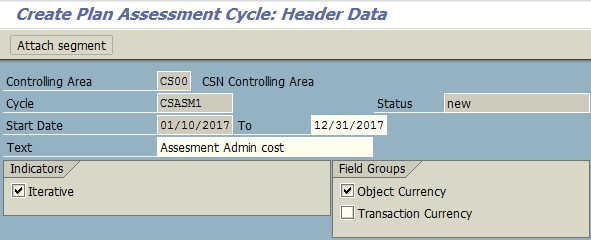
Next, you should assign the secondary cost element, specify sender rules and receiver tracing factor. In many cases, cost assessment can use the allocation structure instead which already consists of allocation rules of sender and receiver. In SAP, that is optional.
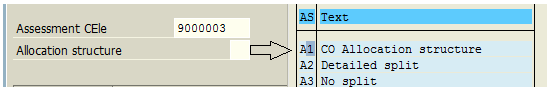
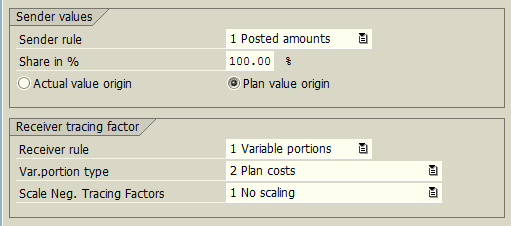
In Sender/Receiver tab, we also assign the sender and receiver values (preferably, cost centers and cost element).
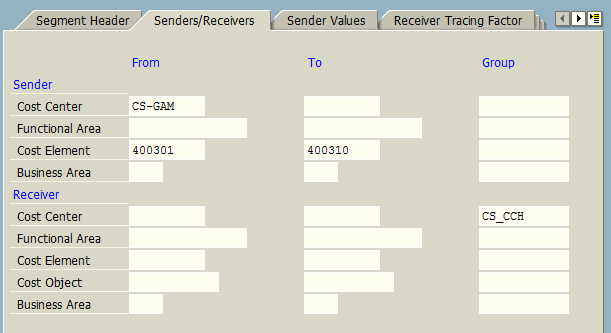
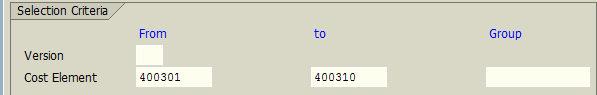
In the Receiver Tracing Factor tab, we provide the list of cost elements. In this example, we selected all cost elements related to administration expenses.
Finally, in the Receiver Weighting Factors tab, we will input the percentage of cost allocation for the related cost receivers. Percentages are generally based on a client’s discretion considering how much indirect cost can be allocated between cost receivers (to each department).
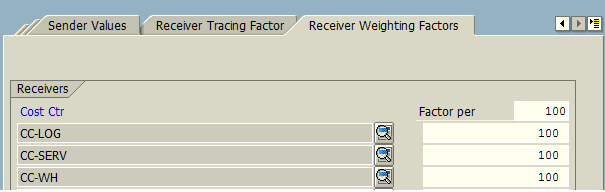
After all the necessary settings, an assessment cycle is saved. Once the assessment cycle is in place, we can use the transaction code KSUB for execution of Plan/Actual assessment as per requirements. The process of execution is the same as for the transaction code KSV5 – Execute Distribution Cycle.
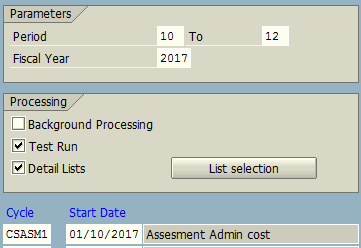
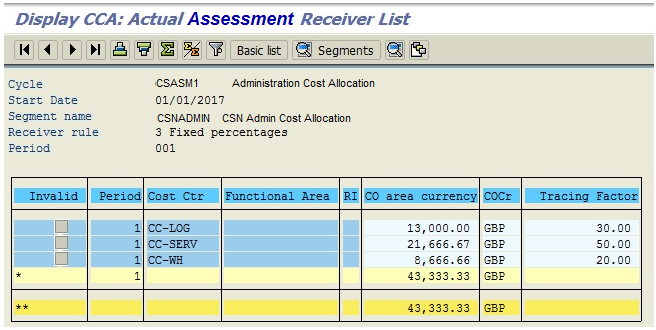
The above screen shows how administration costs are allocated to related cost centers using assessment method of SAP cost allocation based on charging cost through secondary cost element as defined above.

Leave A Comment?
You must be logged in to post a comment.